Elephants are some of the most magnificent creatures on Earth, captivating people from all around the world with their intelligence, size, and beauty. When it comes to elephants, there are two primary species: the African Elephant vs Asian Elephant. While they share similar features, these giant animals also have many differences in terms of behavior, habitat, and conservation efforts.
In this article, we will explore the characteristics that set these two magnificent species apart, shedding light on their strengths, weaknesses, and unique attributes. From size to behavior, we’ll delve into the details that help us better understand and appreciate these majestic creatures.
Jump To
ToggleKey Takeaways
- The African Elephant and Asian Elephant are two primary species of elephants.
- They share similar features like intelligence, size, and beauty.
- The two species have many differences in terms of behavior, habitat, and conservation efforts.
- The African Elephant is larger, while the Asian Elephant has unique physical features like smaller ears.
- Both African and Asian elephants play important roles in maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
Understanding the African Elephant
The African Elephant (Loxodonta africana) is the largest land animal and one of two elephant species. Found throughout sub-Saharan Africa, these magnificent creatures captivate people with their enormous size and distinctive features.
Characterized by their long, curved tusks; large ears; and distinctive trunk, African Elephants stand out as a symbol of strength and intelligence. These animals play a vital role in their ecosystem, helping to maintain the balance of plant and animal populations.
One of the unique characteristics of the African Elephant is its social behavior. These intelligent creatures display complex communication patterns and exhibit empathy and compassion toward their herd members. Additionally, African Elephants are known for their exceptional memory, allowing them to remember their migration routes and water sources for decades.
Despite their importance in maintaining the balance of their ecosystems, African Elephants face numerous threats to their survival. Habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict are all factors that contribute to the declining populations of these remarkable animals.
African Elephant Characteristics
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Size | African Elephants are the largest land animals, weighing up to 6 tons. |
| Tusks | African Elephants have long, curved tusks used for foraging, defense, and communication. |
| Trunk | Their trunk is a remarkable appendage that serves as a versatile tool for drinking, smelling, and communicating. |
| Social Behavior | African Elephants are social animals that live in matriarchal herds, displaying complex communication patterns and empathy toward herd members. |
| Diet | African Elephants consume a variety of vegetation, including grasses, leaves, fruits, and bark. |
Despite the numerous challenges that African Elephants face, there are ongoing efforts to protect and conserve these magnificent creatures. By understanding their unique characteristics and roles in their ecosystem, we can better appreciate and advocate for the preservation of these awe-inspiring animals.
Uncovering the Asian Elephant
The Asian Elephant (Elephas maximus) is one of the three remaining elephant species and the second-largest land mammal after its African counterpart. While they may not surpass their African cousins in terms of size, Asian elephants have their own set of fascinating characteristics that distinguish them.
Distinct Characteristics of the Asian Elephant
Unlike African elephants, Asian elephants have smaller ears, rounder backs, and smoother skin with less hair. They also possess a single “finger” at the tip of their trunk that enables them to pick small objects with precision.
Moreover, an Asian elephant’s tusks are smaller and thinner, with some individuals not having them at all. This is due to the fact that elephants’ ivory tusks are a result of sexual selection, with males having larger tusks to attract females during mating season. Since Asian elephants live in smaller herds than African elephants, there is less competition among males hence smaller tusks.
Behavior and Adaptation
Asian elephants are highly social animals with a complex hierarchy within their herds. They work together to care for their young, protect their territory from predators, and share resources such as food and water. In the wild, they have been observed to use tools like sticks to scratch themselves or swat flies, as well as swim and dive in bodies of water.
Due to habitat fragmentation and loss, Asian elephants have adapted to living in a wide range of habitats, including tropical and subtropical forests, grasslands, and even near human settlements.
Conservation Status
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), Asian elephants are considered an endangered species, with only 40,000-50,000 individuals remaining in the wild. Habitat loss, poaching for their ivory tusks, and human-elephant conflicts are the main threats to their survival.
Efforts to conserve and protect Asian elephants include the creation of protected areas, conservation education, and encouraging sustainable tourism practices that benefit local communities and promote elephant conservation.
Asian Elephant vs African elephant : A Comparison of Size
When it comes to size, African and Asian elephants have some notable differences. African elephants are known to be the largest land animals on earth, growing up to 13 feet tall at the shoulder and weighing around 6,000 kg for males and 3,000 kg for females. The Asian elephant, on the other hand, grows up to 9 feet tall and typically weighs between 2,000 – 5,500 kg for males and 1,500 – 2,700 kg for females.
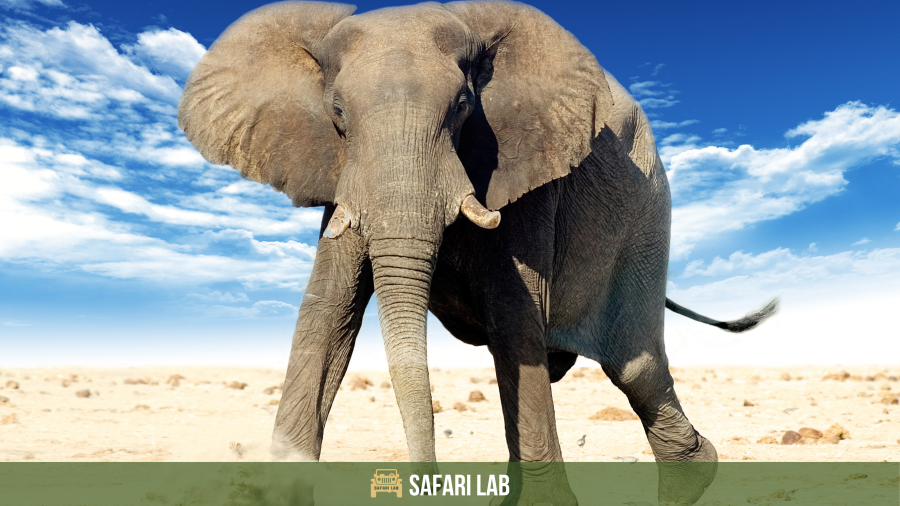

While both elephants are giants in their own right, the African elephant is substantially larger than its Asian cousin. In addition to size, the two species also have some differences in their physical features, such as the shape and size of their ears and tusks.
African Elephant vs Asian Elephant – Contrasting Behaviors
Despite the similarities in appearance, African and Asian elephants demonstrate unique behavior patterns that are shaped by their respective environments and social structures.
African elephant behavior: These elephants are generally more social than their Asian counterparts. They live in herds, which can consist of up to 100 individuals, and exhibit complex communication methods that involve vocalizations, body language, and touch. African elephants are known for their intelligence, empathy, and ability to mourn their dead.
Asian elephant behavior: Asian elephants are typically more solitary compared to African elephants. They form smaller herds with a matriarchal social structure, where the oldest and largest female leads the group. They communicate via vocalizations, touch, and visual cues and demonstrate exceptional memory and problem-solving skills.
It is important to note that both African and Asian elephants have been observed exhibiting extraordinary behaviors, such as using tools, showing altruism, and displaying emotional intelligence.
“Elephants can live together harmoniously and work cooperatively to solve problems. Their ability to empathize is extraordinary and highlights their complex emotional lives.”
Communication Methods
Elephants have a variety of communication methods, including vocalizations, touch, body language, and visual cues.
| Communication Method | African Elephant | Asian Elephant |
|---|---|---|
| Vocalizations | African elephants use a wide range of vocalizations to communicate with their herd members, including trumpets, grunts, roars, and rumbles. These sounds can travel up to 6 miles away, allowing elephants to communicate across long distances. | Asian elephants use a similar range of vocalizations, but their frequencies are generally higher and may be inaudible to humans. They also produce distinct rumbling sounds known as “pig grunts” by holding air in their trunks and releasing it. |
| Touch | African elephants are known to touch each other with their trunks and other body parts. They use touching for social bonding, comfort, and communication. | Asian elephants also touch each other with their trunks, but they have a unique behavior of intertwining their trunks as a sign of affection or greeting. |
| Body Language | African elephants use their body language to communicate various emotions and signals, such as flapping their ears, raising their trunks, or swishing their tails. | Asian elephants also use their body language to communicate different meanings, such as extending their trunks as a greeting or sign of submission. |
| Visual Cues | African elephants have expressive eyes and rely on visual cues to signal various emotions, such as fear, anger, or excitement. They also recognize themselves and others in mirrors. | Asian elephants have smaller eyes compared to African elephants and use body language more than visual cues to communicate their messages. |
African Elephant vs Asian Elephant – Diverse Habitats
African and Asian elephants are two distinct species that inhabit different regions and have adapted to varying landscapes and climates. African elephants are found in sub-Saharan Africa, primarily in savannahs, grasslands, forests, and deserts. In contrast, Asian elephants have a wider range that extends from India to Southeast Asia, where they can be found in forests, grasslands, and scrublands.
Their differing habitats have a significant impact on their lifestyle and behavior. African elephants, for example, rely on open savannahs and water sources during the dry season and move to forested areas during the wet season. In contrast, Asian elephants require dense vegetation and access to water sources year-round and seasonally migrate in search of food and water.
African Elephant Habitat
African elephants can be found in a range of habitats, including:
| Habitat Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Savannahs | African elephants are well-adapted for life on the savannah, where they can easily access water sources and forage for grasses, herbs, and shrubs. |
| Forests | Elephants occupy forested areas during the wet season, where they can access water sources and find fresh vegetation. In these areas, they also create pathways that benefit other wildlife. |
| Deserts | While African elephants are not commonly found in desert areas, some populations exist in arid regions such as Namibia and Mali. In these areas, they rely on water sources and the sparse vegetation available. |
Asian Elephant Habitat
Asian elephants are primarily found in forested areas, but their habitats can vary depending on their location:
| Habitat Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Forests | Asian elephants rely on forested areas for food, water, and shelter and are well-adapted to life in dense vegetation and mountainous areas. |
| Grasslands | Some populations of Asian elephants can also be found in open grasslands and scrublands, where they feed on grasses and herbs. An example is the Jim Corbett National Park and Kaziranga National Park. |
| Wetlands | Asian elephants living in southern India and Sri Lanka can be found in wetland habitats, where they can access freshwater sources and find vegetation year-round. |
Understanding the differences between African and Asian elephant habitats is crucial for ensuring the conservation and survival of these magnificent animals. Conserving and protecting their habitats is essential for safeguarding their populations and the entire ecosystem in which they live.
Conservation Efforts
Both the African and Asian elephant species have been the subject of conservation efforts due to the threats posed by habitat loss and human activities such as poaching. However, the strategies employed for the conservation of these two species differ in significant ways.
For instance, African elephants are typically hunted for their ivory tusks, which are in high demand globally. The African Elephant Coalition (AEC) has been fighting hard to end illegal ivory trade and strengthen the African Elephant Action Plan to provide a framework for countries to work together to conserve elephants and stop ivory trade. In contrast, Asian elephants face threats such as habitat loss, human-elephant conflict, and mistreatment for tourism and entertainment purposes. Conservationists have been working to address these issues directly by partnering with forest departments to enhance elephant corridors and implement compensation schemes for communities that face crop damage or personal injuries from elephants.
Conservation Initiatives: A Comparative Overview
| African Elephant | Asian Elephant | |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Challenges | Poaching for ivory, habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict | Habitat loss, human-elephant conflict, mistreatment for tourism and entertainment |
| Conservation Initiatives | The African Elephant Coalition (AEC), the African Elephant Action Plan | Partnering with forest departments, compensation schemes for affected communities, education and awareness programs |
| Population Status | Declining | Endangered |
As the table shows, while both African and Asian elephants face significant challenges, such as habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict, each species requires tailored conservation approaches. These approaches must be implemented by concerned parties and relevant ecosystem stakeholders to ensure that both elephant species continue to thrive in their respective habitats.
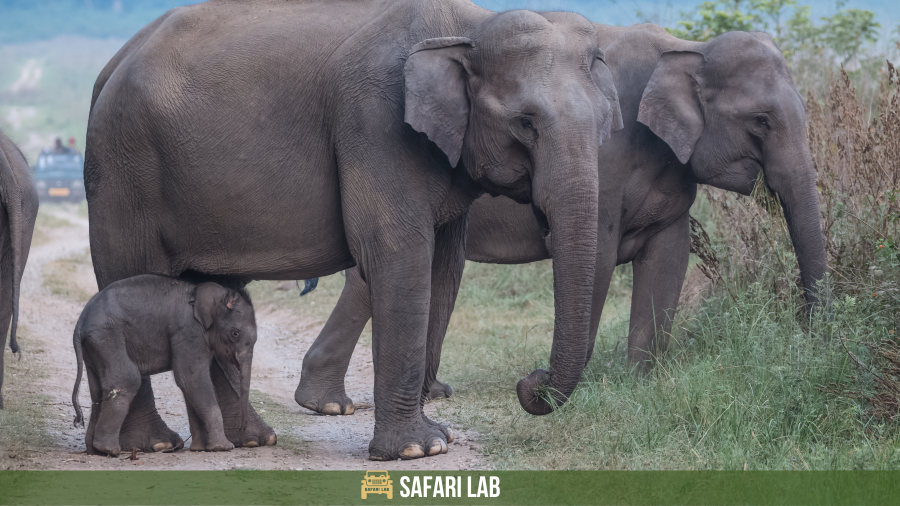

Asian Elephants vs African Elephants – Importance in Ecosystems
African and Asian elephants are keystone species that play critical roles in their respective habitats. These majestic creatures are known to shape their environments in numerous ways, contributing to the balance and biodiversity of their ecosystems.
One of the ways in which elephants impact their ecosystems is through their feeding habits. African elephants, for instance, are known to eat a wide variety of vegetation, which helps to maintain the balance of plant species in their habitats. Asian elephants, on the other hand, consume less vegetation and rely more on woody plants, contributing to the maintenance of forest ecosystems.
Elephants also play an important role in maintaining the soil structure and nutrient composition of their habitats. Their dung serves as a source of nutrients for other animals and plants, while also helping to spread the seeds of plants that make up their diet.
Furthermore, elephants contribute to the overall biodiversity of their ecosystems by creating and maintaining habitats for other species. They are known to dig water holes, create trails, and remove invasive species, all of which help to maintain healthy habitats for other animals.
African vs Asian Elephant: Contrasting Roles in Ecosystems
| African Elephant | Asian Elephant | |
|---|---|---|
| Feeding Habits | Eat a wide variety of vegetation | Consume less vegetation, rely more on woody plants |
| Dung | Serves as a source of nutrients for other animals and plants | Helps to fertilize soils and spread seeds of woody plants |
| Creating Habitats for Other Species | Create open savanna habitats by knocking down trees and clearing bushes | Create and maintain forest ecosystems by opening up gaps in the canopy and creating clearings |
Overall, African and Asian elephants are critical components of their ecosystems, playing unique and vital roles in maintaining the balance and biodiversity of their habitats.
Cultural Significance – African Elephant vs Asian Elephant
Elephants hold an important place in both African and Asian cultures, with significant symbolic and spiritual value. In Africa, the African Elephant is seen as a symbol of strength, wisdom, and power. Many African tribes incorporate elephants in their traditions and rituals, believing that they possess spiritual qualities.
Similarly, in Asian cultures, especially Hinduism and Buddhism, the Asian Elephant is considered sacred and holds a deep religious significance. The god Ganesha, one of the most revered deities in Hinduism, is depicted with the head of an elephant, symbolizing wisdom and knowledge. Moreover, in Buddhist teachings, the white elephant is an important religious symbol and is believed to have carried the Buddha’s mother in her dream, foretelling the birth of Buddha.
“The elephant is a symbol of what humans need to be in the world. They are generous, cooperative, intelligent, empathetic, wise and self-aware,” – Joyce Poole, African Elephant expert.
These majestic creatures have also had a prominent role in art and literature, with many ancient texts and sculptures featuring elephants. Today, elephants continue to inspire artists, writers, and photographers, making their way into contemporary art and culture.
Despite their cultural significance, both African and Asian elephants have suffered due to human activities such as poaching and habitat loss, emphasizing the urgent need to protect these magnificent animals.
Fun Facts about Elephants
Here are 10 fun facts about elephants:
- Size and Weight: Elephants are the largest land animals on Earth, with males reaching up to 12 feet in height and weighing up to 14,000 pounds. Elephants are not only the largest land animals, but they also have the longest gestation period of any mammal, lasting about 22 months.
- Trunks: An elephant’s trunk contains over 40,000 muscles, which makes it incredibly strong and versatile, allowing the elephant to pick up objects as small as a coin or as large as a tree branch. Elephants use their trunks for various tasks, including breathing, drinking, trumpeting, and foraging for food.
- Communication: Elephants are known for their complex communication abilities, using a variety of sounds, body language, and infrasound to convey messages over long distances. They can communicate with each other using a wide range of vocalizations, including trumpeting, rumbling, and roaring.
- Memory: Elephants have impressive long-term memories and are known to recognize and remember individual elephants even after many years of separation. Their exceptional memory helps them navigate their environment and remember locations of water sources and food.
- Social Structure: Elephants live in a matriarchal society, led by the oldest and most experienced female in the herd, who makes important decisions for the group. The bond between elephants in a herd is strong, and they display empathy and mourn their dead, showing a deep emotional intelligence.
- Diet: Elephants are herbivores and can consume up to 300 pounds of food in a single day, consisting of grasses, leaves, bark, and fruits. They play a crucial role in shaping their environment through their feeding habits, which can help maintain the balance of ecosystems.
- Intelligence: Elephants are highly intelligent animals, capable of problem-solving, showing self-awareness, and even displaying artistic abilities. They have been observed using tools, such as using branches to swat flies or scratching themselves with sticks.
- Life Span: Elephants have a long lifespan, with an average of 60-70 years in the wild, and they develop strong bonds within their family groups over these years. The bond between family members, especially between a mother and her calf, is particularly strong and lasts a lifetime.
- Speed: Despite their large size, elephants can reach speeds of up to 25 miles per hour when running, making them surprisingly fast. While they may not be the fastest runners, their speed is impressive considering their massive build.
- Conservation: Elephants are considered keystone species in their habitats, playing a crucial role in maintaining the biodiversity of the ecosystems they inhabit. Their presence has a significant impact on the environment, and their conservation is essential for the well-being of many other species that share their habitatAfter comparing the African Elephant vs Asian Elephant, we can appreciate the distinctive features and characteristics of each species. The African Elephant, known for its enormous size and majestic presence, inhabits vast savannas, while the Asian Elephant thrives in dense forests.
Conclusion
Both species play crucial roles in their ecosystems, with African Elephants shaping the landscape and Asian Elephants contributing to forest regeneration. However, both face numerous conservation challenges due to habitat loss and human activities such as poaching and deforestation.
By understanding and appreciating the unique qualities of African and Asian Elephants, we can better appreciate the importance of their conservation. Whether it’s through education, advocacy, or conservation efforts, we can work together to ensure that these magnificent creatures continue to thrive for generations to come.
In conclusion, both African and Asian Elephants are awe-inspiring creatures that deserve our admiration and protection. By recognizing their differences and similarities, we can gain a deeper understanding of the beauty and complexity of the natural world.
FAQ
What are the main differences between African and Asian elephants?
African and Asian elephants differ in several ways, including their size, behavior, habitat, and conservation efforts.
What are the characteristics of the African Elephant?
The African Elephant is the largest land animal, known for its enormous size, long tusks, and distinctive features. They have large ears and two finger-like projections at the tip of their trunk.
How does the Asian Elephant differ from the African Elephant?
The Asian Elephant is smaller in size compared to the African Elephant. It has smaller ears, a more rounded back, and only one finger-like projection at the tip of its trunk.
How do African and Asian elephants compare in terms of size?
African elephants are larger than Asian elephants. On average, male African elephants can weigh up to 12,000 pounds and stand around 10-13 feet tall at the shoulder, whereas male Asian elephants weigh around 5,500-11,000 pounds and stand about 8-10 feet tall at the shoulder.
How do African and Asian elephants differ in behavior?
African elephants are known to live in more extensive social groups and exhibit a greater degree of aggression compared to Asian elephants. Asian elephants tend to have a more peaceful nature and form smaller family units.
What are the main differences in habitat between African and Asian elephants?
African elephants are found across sub-Saharan Africa, where they inhabit a variety of habitats, including savannas, forests, and grasslands. Asian elephants, on the other hand, are primarily found in the tropical and subtropical forests of South and Southeast Asia.
What conservation efforts are being made for African and Asian elephants?
Both African and Asian elephants face conservation challenges due to habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflicts. Conservation organizations and governments are implementing various measures to protect and preserve these species, including anti-poaching initiatives, habitat conservation, and community-based conservation programs.
What is the importance of African and Asian elephants in ecosystems?
African and Asian elephants play vital roles in their ecosystems. They are considered keystone species, playing a crucial part in shaping habitats through their feeding habits and seed dispersal. They help maintain the balance of vegetation and create essential water sources for other animals.
What cultural significance do elephants hold?
Elephants have significant cultural and historical importance in both African and Asian societies. They symbolize strength, wisdom, and are often featured in traditional art, folklore, and religious ceremonies.
Recent Posts
Archives
Categories
Customized Trip Form
Author

Sanjay Nair is a multi-award-winning wildlife photographer, conservation storyteller, and co-founder of Safari Lab. With over 15 years of fieldwork and a Nature in Focus award under his belt, Sanjay’s photographs and stories have been published in global outlets such as The Times & The Guardian.
View all posts