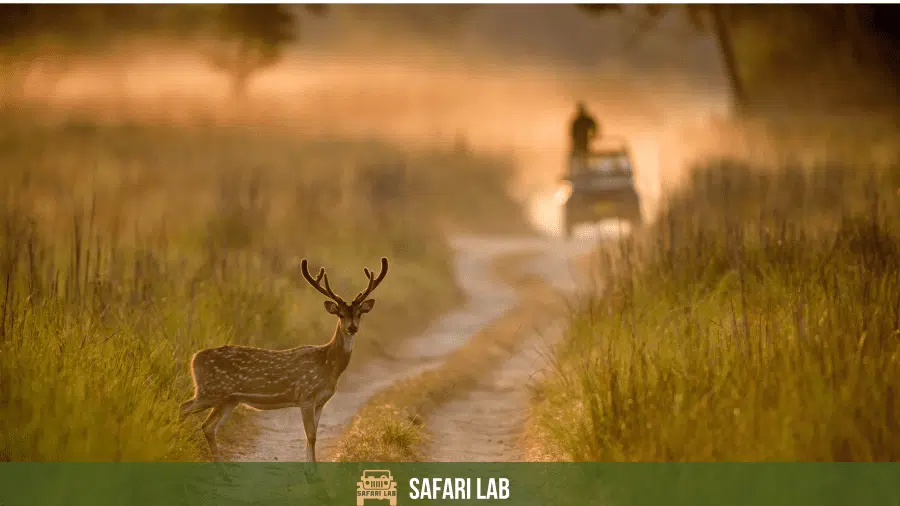
The Indian Bison, also known as the Gaur, is the largest bovine species in Asia. It is native to South and Southeast Asia and is often mistaken for the American Bison, but they are two distinct species. The Indian Bison has a massive build, with males standing up to 2.2 meters tall at the shoulder. It has a glossy black coat, muscular physique, and curved horns. Indian Bison populations are mainly found in India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, Thailand, and other Southeast Asian countries.
Jump To
ToggleKey Takeaways:
- The Indian Bison, or Gaur, is the largest bovine species in Asia.
- It has a massive build with males standing up to 2.2 meters tall at the shoulder.
- Indian Bison populations are mainly found in South and Southeast Asia.
- The Indian Bison is often mistaken for the American Bison, but they are two distinct species.
- Indian Bison can be found in India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, Thailand, and other Southeast Asian countries.
Indian Bison Habitat and Behavior
The Indian Bison, also known as the Gaur, thrives in a variety of forest habitats, including tropical evergreen forests, bamboo forests, and dry deciduous forests. They prefer hilly terrain and can be found at elevations up to 2,800 meters. This adaptable species has managed to establish populations in different regions of India, Bhutan, and Bangladesh.
With an estimated population of 23,000 to 34,000 individuals, Indian Bison live in herds of up to 12 individuals. They exhibit fascinating behavior, such as forming circular sleeping formations where the calves are protected in the center. These intelligent creatures are known for their generalist feeding habits, consuming grass, leaves, bamboo, fruits, and other vegetation.
Although generally shy, Indian Bison can become dangerous if provoked or threatened. They display a strong sense of social structure within their herds, with dominant individuals leading and protecting the group.
“Indian Bison, or Gaurs, are magnificent creatures that have adapted to various habitats and exhibit highly unique behaviors. As a generalist feeder, the Bison plays a crucial role in the balance of ecosystems.”
Indian Bison Population
The population of Bison is scattered across different locations, primarily in India, Bhutan, and Bangladesh. While the exact numbers can be challenging to determine accurately, recent estimates suggest a population ranging from 23,000 to 34,000 individuals.
Indian Bison Habitat
Bison are well-suited to survive in a range of forest habitats, including:
- Tropical evergreen forests
- Bamboo forests
- Dry deciduous forests
They are particularly adapted to hilly terrains and are known to inhabit elevations of up to 2,800 meters above sea level.
Indian Bison Behavior
Indian Bison exhibit fascinating behavior patterns within their herds, such as:
- Forming circular sleeping formations with calves protected in the center
- Establishing a social structure with dominant individuals leading and protecting the group
While generally shy and peaceful, Bison can become dangerous if provoked or threatened.
| Keyword | Indian Bison Habitat | Indian Bison Population | Bison Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indian Bison habitat | Tropical evergreen forests, bamboo forests, dry deciduous forests | 23,000 – 34,000 individuals | Circular sleeping formations, social structure within herds |
Indian Bison Conservation Efforts
The Indian Bison, also known as the Gaur, is facing significant conservation challenges. Listed as an endangered species under the Indian Wildlife Protection Act 1972, and categorized as vulnerable by the IUCN, urgent action is needed to protect this magnificent species from further decline.
The primary threats to Bison populations are habitat loss and contagious diseases, such as rinderpest and anthrax. Deforestation, encroachment, and infrastructure development have led to the degradation and fragmentation of their habitats. These factors have resulted in the loss of suitable feeding and breeding grounds for the Bison.
Efforts are underway to conserve and restore Bison populations. Reintroduction projects and the establishment of protected areas like national parks and wildlife sanctuaries have been initiated to safeguard their survival.
“Conservation is crucial to protect the Bison species and preserve the biodiversity of the ecosystems they inhabit,” says Dr. Priya Sharma, a renowned wildlife biologist.
In Bandhavgarh National Park, a successful reintroduction project has demonstrated the potential for reviving Bison populations. By carefully monitoring their habitat, implementing anti-poaching measures, and raising awareness about their conservation needs, the park has witnessed a significant increase in the number of Indian Bison individuals.
Furthermore, community participation and government support are essential for the success of Indian Bison conservation. Engaging local communities in conservation efforts helps foster a sense of ownership and promotes sustainable practices that benefit both the Bison and the surrounding ecosystems.
Indian Bison Conservation Initiatives:
- Reintroduction projects in key habitats
- Establishment of protected areas
- Increased anti-poaching efforts
- Community engagement and education
- Raising awareness about the ecological importance of Bison
By focusing on these conservation initiatives, we can work towards ensuring a brighter future for the Indian Bison species. Through collaborative efforts, we can protect their habitats, mitigate threats, and secure the survival of this iconic bovine species for generations to come.
| Conservation Measures | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Reintroduction projects | Revive populations in depleted areas |
| Protected areas | Provide safe habitats for Bison |
| Anti-poaching efforts | Reduce illegal hunting and trade |
| Community engagement | Promote sustainable practices and conservation awareness |
| Education and awareness | Foster public support for Indian Bison conservation |
By valuing and protecting the Bison, we not only preserve a magnificent species but also safeguard the intricate balance of the ecosystems they inhabit. Our collective effort is crucial in securing the future of the Bison and the rich biodiversity they represent.
Indian Bison Diet and Feeding Habits
The Bison, being a herbivore, has a diverse diet that plays a crucial role in shaping its feeding habits and the ecosystems it inhabits. Its diet includes:
- Grass
- Leaves
- Shoots
- Buds
- Bamboo
- Herbs
- Fruits
Additionally, Bison rely on salt licks to fulfill their mineral needs. Feeding takes up a significant portion of their day, with the animals spending around 10 to 15 hours engaged in feeding activities. Their diet leads them to travel considerable distances in search of food, influencing the distribution and abundance of plant species within their range.
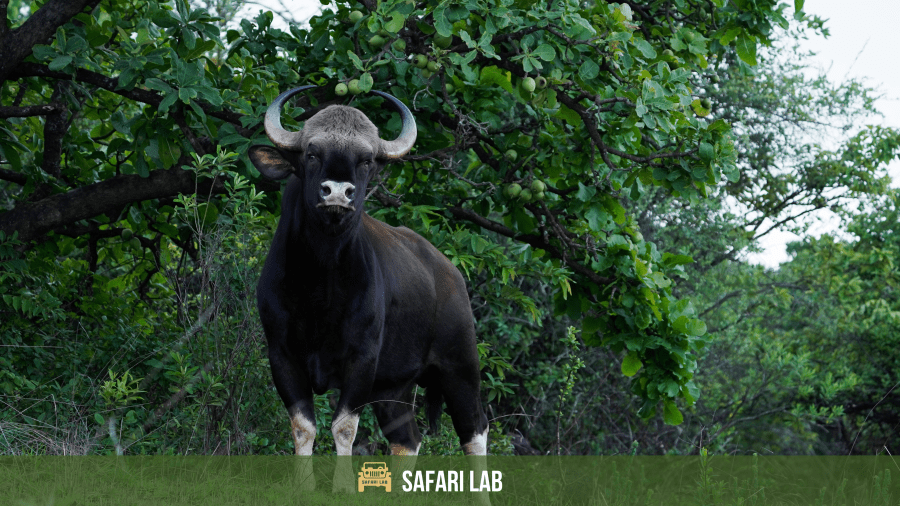

“The Indian Bison’s feeding habits have a significant impact on the ecosystems they inhabit, influencing the distribution and abundance of plant species in their range.”
Feeding Habits and Ecosystem Impact
The Indian Bison’s feeding habits have ecological implications for the wildlife and vegetation in their habitat. As grazers, Bison contribute to the grazing pressure on grasslands, controlling the growth of certain plant species and creating open spaces for other vegetation to flourish. By consuming leaves, shoots, and buds, they also influence the regeneration of forests and maintain a balanced ecosystem.
Their feeding habits can shape the landscape and contribute to the overall biodiversity of their habitat. As a keystone species, their presence and feeding activities have a cascading effect on the wildlife community, influencing the abundance and behavior of other species such as herbivores, predators, and scavengers.
Table:
| Dietary Items | How it shapes the ecosystem? |
|---|---|
| Grass | Controls grassland growth and creates open spaces for other vegetation |
| Leaves, Shoots, Buds | Influences forest regeneration and maintains a balanced ecosystem |
| Bamboo | Affects the spread and growth of bamboo forests |
| Herbs, Fruits | Provides nutrition and disperses seeds, contributing to plant diversity |
This table illustrates how the Indian Bison’s diet contributes to the shaping of the ecosystem, highlighting the critical role they play as herbivores in maintaining a diverse and balanced environment.
Indian Bison in Different Regions
Indian Bison, also known as Indian Gaur, have distinct regional populations in different parts of their range. These majestic creatures thrive in various regions across India and Bhutan, contributing to their conservation efforts.
Indian Bison in India
In India, the Central Indian Highlands, Eastern Ghats, and Western Ghats are major regions where Indian Bison thrive. National parks like Tadoba, Kanha, and Periyar offer excellent opportunities for wildlife enthusiasts to observe these magnificent animals in their natural habitat.
Indian Bison in Bhutan
In Bhutan, Royal Manas National Park and other protected areas support the population of Indian Bison, also known as Indian Gaur. These regions provide important habitats for the Indian Bison and play a vital role in their conservation efforts.
By preserving these regions and their unique ecosystems, we can ensure the continued survival and protection of the Indian Bison, a truly remarkable species.
Unique Facts About Indian Bison
Indian Bison, or Gaurs, are fascinating creatures with unique characteristics and behaviors. Let’s explore some interesting facts about these majestic giants:
1. The “Moo” that Travels
Indian Bison have a distinctive call, known as the “moo,” which can travel up to 1.5 kilometers. This vocalization serves as a communication tool among herd members and helps maintain social cohesion.
2. Changing Colors
As Indian Bison grow, they undergo dramatic color changes. Newborn calves are golden yellow, providing them with camouflage in their grassy habitat. However, as they mature, their coats gradually change to brown. Male Indian Bison turn jet black as adults, while females retain a slight brown pelage.
3. Lateral Displays and High-Pitched Whistles
When threatened or agitated, Indian Bison display fascinating behaviors. They employ lateral displays, where they turn their bodies sideways, showcasing their massive size and intimidating potential rivals. Additionally, they emit high-pitched whistles, alerting the herd to potential danger and serving as a warning signal.
“Indian Bison are known for their distinctive call, color-changing abilities, lateral displays, and high-pitched whistles.”
These unique characteristics make Bison a captivating species, worthy of study and observation. Now, let’s dive deeper into their conservation efforts in the upcoming section.

The Importance of Bison Conservation
The conservation of Bison is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and preserving the ecosystems in which they reside. As a flagship species, the Bison represents the health of the forests and other wildlife populations in their habitat. By protecting Bison populations, we ensure the survival of not only this magnificent bovine species but also the interconnected web of life within their ecosystems.
The Bison, also known as the Gaur, has a significant impact on the surrounding environment. Their feeding habits and grazing behaviors shape the vegetation composition and distribution, influencing the overall landscape and biodiversity. Furthermore, the presence of Bison indicates the ecological integrity of the ecosystems they inhabit, serving as an indicator species of habitat health.
To conserve Bison, various efforts are undertaken. These include:
- The establishment and protection of conservation areas
- The implementation of anti-poaching measures to combat illegal hunting and trade
- The promotion of sustainable land-use practices and habitat restoration
- The dissemination of knowledge and raising awareness about the ecological importance of Indian Bison
“The conservation of Indian Bison not only ensures the survival of a charismatic species but also benefits all other flora and fauna that share their habitat. It is a testament to our commitment to safeguarding our natural heritage.”
Efforts to conserve Indian Bison have significant implications for other species and the overall functioning of ecosystems. When we protect Indian Bison populations, we contribute to the preservation of genetic diversity, the promotion of ecological resilience, and the maintenance of ecosystem services. Additionally, conserving Indian Bison serves as a beacon of hope for the future, inspiring broader conservation efforts and fostering stewardship of our natural world.
| Importance of Indian Bison Conservation | Actions Taken |
|---|---|
| Preserve biodiversity | Establishment of protected areas |
| Maintain ecological balance | Implementation of anti-poaching measures |
| Ensure habitat health | Sustainable land-use practices and habitat restoration |
| Inspire conservation | Knowledge dissemination and awareness campaigns |
The Role of Indian Bison as a Flagship Species
Indian Bison’s charismatic presence and ecological significance make them ideal flagship species for conservation efforts. As an ambassador for their habitat, the Indian Bison can attract attention, resources, and public support to protect not only themselves but also the entire ecosystem they inhabit. By conserving Bison, we address broader conservation challenges and contribute to the preservation of our natural heritage.
Challenges and Future Outlook for Indian Bison Conservation
Despite the dedicated efforts towards Bison conservation, several challenges persist in safeguarding the future of this majestic species. Habitat loss remains a significant threat, primarily due to deforestation, encroachment, and infrastructure development. The destruction of their natural habitats has a direct impact on the Indian Bison population, limiting their range and access to essential resources.
Poaching poses another significant challenge to Bison conservation. Despite strict regulations and anti-poaching measures, the demand for their meat, horns, and other body parts continues to fuel illegal hunting activities. This illegal trade further presses the Bison population, pushing them closer to the brink of extinction.
The threats to Indian Bison are compounded by the effects of climate change and infectious diseases. Changes in temperature, rainfall patterns, and the spread of diseases pose additional risks to their survival. The increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events disrupt their habitats and food sources, making it more challenging for Bison populations to thrive.
To ensure the future of Bison, sustained conservation efforts are vital. This requires the active participation of local communities, who play a crucial role in protecting their natural habitats and mitigating human-wildlife conflicts. Additionally, government support is essential in enforcing regulations, implementing conservation programs, and providing adequate resources for wildlife protection.
Continued research and monitoring are also crucial to inform conservation strategies and effectively protect the Indian Bison. By studying their behavior, population dynamics, and ecological roles, experts can develop targeted interventions and conservation plans tailored specifically for the needs of this iconic species.
In summary, the conservation of Indian Bison is faced with various challenges, including habitat loss, poaching, climate change, and infectious diseases. However, by implementing sustained conservation efforts, engaging local communities, and conducting ongoing research, we can pave the way for a brighter future for these magnificent creatures.
Key Challenges for Indian Bison Conservation
| Challenges | Description |
|---|---|
| Habitat Loss | Deforestation, encroachment, and infrastructure development impacting their natural habitats. |
| Poaching | Illegal hunting driven by the demand for meat, horns, and other body parts. |
| Climate Change | Changes in temperature, rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events affecting their habitats. |
| Infectious Diseases | Spread of diseases posing risks to the health and survival of Indian Bison populations. |
Conclusion
The Indian Bison, also known as the Gaur, plays a vital role in the ecosystems of South and Southeast Asia. With its impressive size, unique behavior, and ecological importance, it is a species that deserves our conservation efforts. By safeguarding their habitats, implementing anti-poaching measures, and raising awareness about their conservation needs, we can contribute to the long-term survival of this majestic wildlife.
Protecting Indian Bison is not just about preserving a single species; it is about preserving the entire ecosystem in which they thrive. As a flagship species, Bison represents the health of the forests and other wildlife populations in their habitat. By ensuring the survival of Bison, we are also protecting the interconnected web of life within their ecosystems.
Together, we can make a difference. By supporting conservation initiatives, we can provide future generations with the opportunity to witness and appreciate the giants of the wild, the Indian Bison. Let us join hands to protect and preserve this magnificent species for the benefit of wildlife and our planet.
FAQ
What is the Indian Bison?
The Indian Bison, also known as the Gaur, is the largest bovine species in Asia.
Where is the Indian Bison found?
The Indian Bison is mainly found in India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, Thailand, and other Southeast Asian countries.
What is the population of Indian Bison?
The population of Indian Bison is estimated to be around 23,000 to 34,000 individuals in India, Bhutan, and Bangladesh.
What is the habitat of the Indian Bison?
The Indian Bison thrives in a variety of forest habitats, including tropical evergreen forests, bamboo forests, and dry deciduous forests.
What is the behavior of the Indian Bison?
Indian Bison live in herds of up to 12 individuals and are known for their circular sleeping formations. They can become dangerous if provoked or threatened.
What does the Indian Bison eat?
Indian Bison are generalist feeders and consume grass, leaves, bamboo, fruits, and other vegetation.
What is the conservation status of the Indian Bison?
The Indian Bison is listed as an endangered species under the Indian Wildlife Protection Act 1972 and is categorized as vulnerable by the IUCN.
What are the major regions for Indian Bison in India?
The Central Indian Highlands, Eastern Ghats, and Western Ghats are major regions where Indian Bison thrive in India.
What are some unique facts about the Indian Bison?
Indian Bison have a distinctive call known as the “moo,” undergo color changes as they grow, and display lateral displays and high-pitched whistles when threatened.
Why is Indian Bison conservation important?
Indian Bison conservation is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and preserving the ecosystems in which they reside.
What are the major challenges for Indian Bison conservation?
The major challenges for Indian Bison conservation include habitat loss, poaching, climate change, and infectious diseases.
Recent Posts
Archives
Categories
Customized Trip Form
Author

Sanjay Nair is a multi-award-winning wildlife photographer, conservation storyteller, and co-founder of Safari Lab. With over 15 years of fieldwork and a Nature in Focus award under his belt, Sanjay’s photographs and stories have been published in global outlets such as The Times & The Guardian.
View all posts